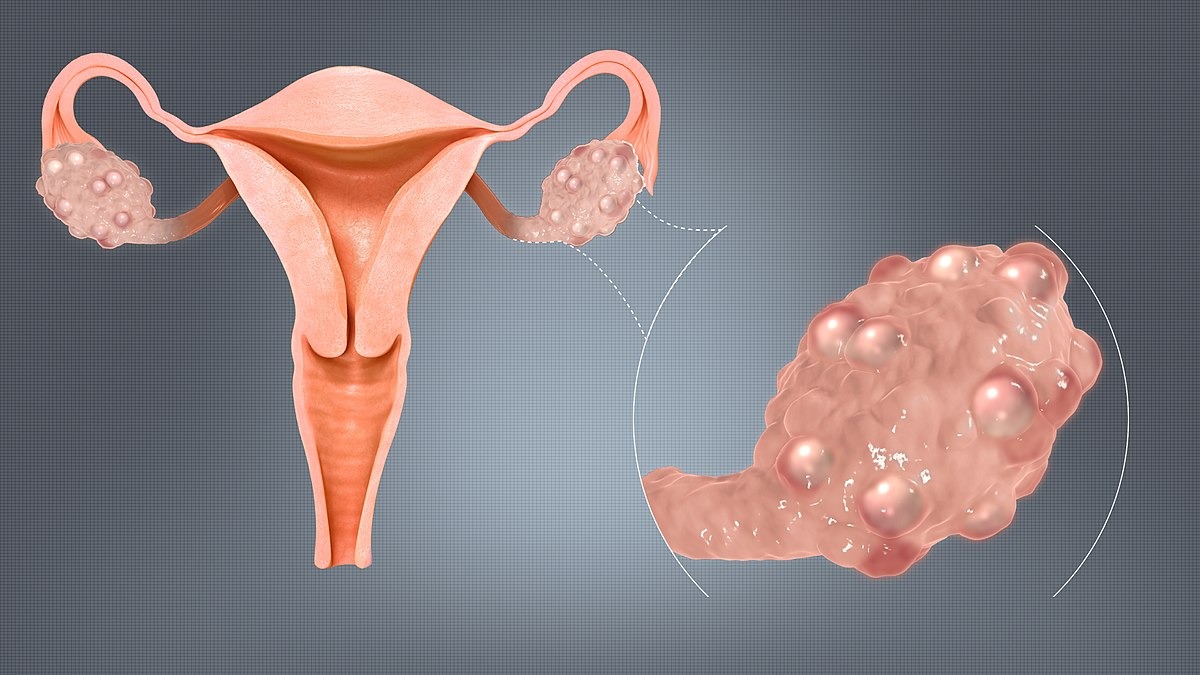
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a prevalent endocrine disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It encompasses a combination of symptoms, including irregular or absent menstrual cycles, elevated levels of androgens (male hormones), and the presence of small fluid-filled sacs (follicles) on the ovaries. Caffeine, a stimulant found in various foods and beverages such as coffee, tea, and chocolate, has long been consumed by humans and offers both positive and negative effects on women with PCOS. In this article, we explore the impact of caffeine on PCOS, shedding light on the potential benefits and drawbacks.
The Positive Effects of Caffeine on PCOS

Research suggests that caffeine consumption may have positive effects on PCOS. A study discovered a correlation between caffeine intake and a decreased risk of developing PCOS. Additionally, the study found that women with PCOS who consumed caffeine exhibited lower levels of androgens and insulin resistance, both of which are characteristic of the condition. Another study revealed that caffeine intake was associated with a more favorable response to PCOS treatment, resulting in regular menstrual cycles and reduced androgen levels.
The Negative Effects of Caffeine on PCOS
While caffeine may offer benefits, some studies indicate potential negative impacts on PCOS. For instance, research demonstrates that caffeine intake may exacerbate insulin resistance and inflammation, both of which can worsen PCOS symptoms. Furthermore, caffeine consumption has been linked to an increased risk of developing metabolic syndrome, a cluster of risk factors associated with heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
See also: Vitamin D and Fatigue
Understanding the Mixed Research Findings
Overall, the research on the impact of caffeine on PCOS presents mixed results. While certain studies suggest positive effects, others highlight potential negatives. Further investigation is necessary to ascertain the long-term effects of caffeine consumption on women with PCOS. Consequently, individuals with PCOS who are concerned about the impact of caffeine should consult their healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Managing Caffeine Intake for PCOS
If you have PCOS and wish to manage your caffeine intake effectively, consider the following tips:
1. Limit Your Intake
Ensure that your consumption of caffeinated beverages remains within a safe range of 400 milligrams per day or less. This is equivalent to approximately four cups of coffee or eight cups of tea.
2. Avoid Late-Day Consumption
Refrain from consuming caffeine late in the day as it can interfere with your sleep patterns, affecting your overall well-being.
3. Observe Personal Reactions
Recognize that individual responses to caffeine vary. Some individuals may be more sensitive to its effects than others. If you notice that caffeine worsens your PCOS symptoms, it might be worth reducing or eliminating your intake to alleviate discomfort.
Caffeine consumption can have both positive and negative implications for individuals with PCOS. While some studies suggest potential benefits such as a lower risk of developing PCOS and improved treatment response, others indicate drawbacks such as increased insulin resistance and a higher risk of metabolic syndrome. As the research on this topic remains inconclusive, it is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider regarding the impact of caffeine on your specific situation. By managing your caffeine intake appropriately, you can take control of your PCOS symptoms and work towards improving your overall well-being.















Add Comment